Map
Introduction
A map node applies a given function to each of its inputs and returns the transformed data. map returns one row for every row of input. Refer to map API for more details.
The figure below illustrates how map applies the transformation to each row of inputs.
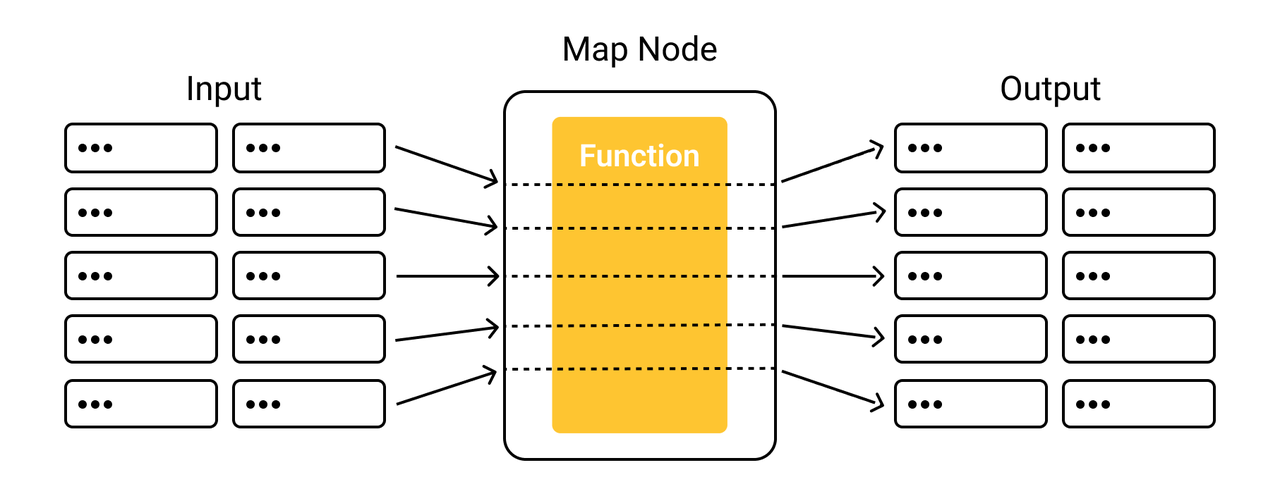
Example
We use the map(input_schema, output_schema, fn, config=None) interface to create a map node.
Note that the input of the fn function should follow the input_schemawhile the output of the fn function should follow the output_schema. Multiple pairs of inputs and outputs of the function mean multiple columns of data in the source and corresponding target table.
Now let's take an text feature extraction pipeline as an example to demonstrate how to use a map node.
This example defines a pipeline for text feature extraction.
When running the pipeline, you can use batch (batch_inputs) to insert multiple rows of data at a time.
from towhee import pipe, ops
text_embedding = (pipe.input('text')
.map('text', 'embedding', ops.sentence_embedding.transformers(model_name='all-MiniLM-L6-v2'))
.output('text', 'embedding')
)
data = ['Hello, world.', 'How are you?']
res = text_embedding.batch(data)
The DAG of the text_embedding pipeline is illustrated below. Texts on the arrows in the image describes how data is transformed by each node. Outputs of a node is highlighted.
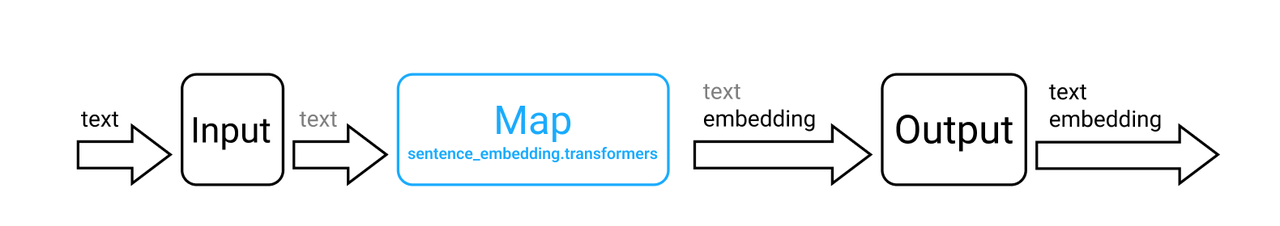
Data transformation in each node is illustrated below.
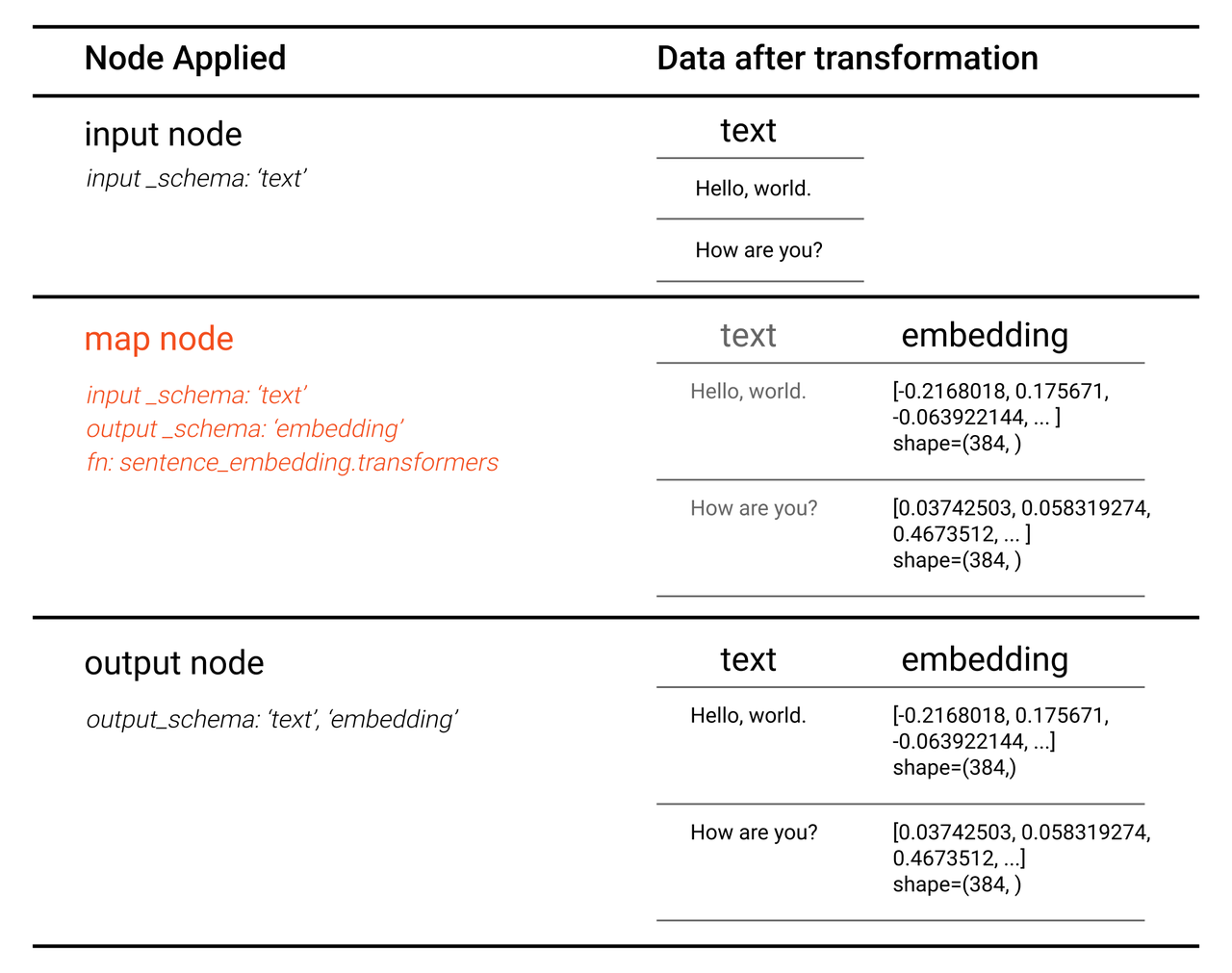
There is one map node in this pipeline.
- map('text', 'embedding', ops.sentence_embedding.transformers(model_name='all-MiniLM-L6-v2'))
This node applies sentence_embedding/transformers operator to text to extract text features and generate sentence embeddings. The operator returns a list of embeddings (embedding) as output.